TEQSA
Australia’s independent national quality assurance and regulatory agency for
higher education is the Tertiary Education Quality and Standards Agency (TEQSA).
Their objective is to safeguard students’ interests and the reputation of
Australia’s higher education sector by using a proportionate, risk-based
approach to quality assurance that encourages diversity, creativity, and
excellence.
TEQSA requires that all organisations that provide higher education credentials
in or from Australia be registered.
Public and private universities, Australian subsidiaries of overseas
universities, and other institute of higher educations make up Australia’s
higher education sector. Higher education institutions deliver degrees ranging
from bachelor’s degrees and associate degrees to advanced diplomas and
postgraduate degrees (graduate certificates and diplomas, masters and doctoral
degrees).
What is Higher education?
Higher education, also known as tertiary education, includes diplomas, advanced
diplomas, associate degrees, bachelor degrees (including honours), graduate
certificates, graduate diplomas, masters degrees, undergraduate degrees, and
higher doctoral degrees, which cover the Australian Qualifications Framework
(AQF) levels 5-10.
View IHM in National Register
AHPRA
The Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA) partners with the 15
National Boards to regulate Australia’s licensed health practitioners in order
to protect the public. Their aim is to protect the public by establishing
guidelines and policies that must be followed by all licensed health
practitioners. Each Board has a health profession agreement with Ahpra that
specifies fees, budgets, and Ahpra’s services.
What they do?
Across all professions registered under the National Registration and
Accreditation Scheme, Ahpra partnered with 15 National Boards to ensure the
public has access to a safe health workforce. Their top goal is still public
safety. The Health Practitioner Regulation National Law (the National Law),
which is in effect in each state and territories, guides any decision they make.
The regulatory duties of Ahpra are as follows:
- Professional Standards – They advise the National Boards on
registration requirements, rules, and guidance for health practitioners.
- Registration – They ensure that only health professionals
with the expertise and credentials to deliver professional and responsible
services are registered to practice in partnership with the National Boards.
APHRA also oversees the registration and renewal of eligible health
practitioners from both the local and overseas, as well as student
registration.
- Compliance – APHRA monitors and checks registered health
practitioners to ensure that they are following the Board’s rules.
- Accreditation – They collaborate with accreditation
authorities and committees to ensure that graduate students are qualified
and professional enough to qualify for health practitioner registration.
APHRA publishes a national Register of Practitioners so that the public has
access to relevant information about particular health practitioners.
IHEA
The Independent Higher Education Association (IHEA) represents the bulk of
Australia’s licensed and certified independent institute of higher educations.
More than 130,000 students and 120 universities make up Australia’s independent
higher education sector, with independent providers approved to offer courses
across the entire AQF spectrum (diplomas up to doctorates).
Higher education institutions that are members of the IHEA educate domestic and
foreign students in undergraduate and postgraduate programs. Major independent
institutions, colleges, business schools, niche providers, and professional
associations with for-profit and non-profit business models make up their varied
membership . IHEA members have a variety of accredited higher education degrees,
ranging from bachelor’s degrees to doctoral degrees.
The Tertiary Education Quality Standards Agency, the Australian government’s
regulator of all universities and institute of higher educations, have
registered and accredited all members. For Australian independent providers,
membership in the IHEA is a mark of excellence.
The IHEA’s Code of Good Practice, which is based on regulatory enforcement, sound
governance, fair business models, quality teaching, and student participation,
is a requirement for membership.
HEPP- QN
Through the power of collaboration, HEPP-QN aims to promote an improved
private-provider efficiency footprint in the Australian market. The network was
officially unveiled on April 21, 2015, at the Avondale Sydney campus in
Wahroonga, with 17 of the 35 affiliate institutions in participation.
They are primarily concerned with assisting one another in the development and
implementation of quality assurance frameworks through their higher education
operations. Their goal is to be proactive and attentive in dealing with the
industry’s urgent and critical issues.
PURPOSE: Developing and extending a PRIVATE PROVIDER HE QUALITY FOOT-PRINT
DESE
The Australian Higher Education Graduation Statement (AHEGS) is a simple,
easy-to-read document that contains information about a student’s higher
education qualification, the university where the qualification was obtained,
and the Australian higher education system.
In consultation with the higher education community, guidelines for presenting an
AHEGS were established to provide information to organizations planning to adopt
the AHEGS. The purpose, relationship to other documents, content and style,
issuing and authentication of the AHEGS are all defined in these guidelines.
Advance HE
Advance HE is a member-led, sector-owned charity that partners with universities
and higher education around the world to enhance the quality of higher education
for faculty, students, and community.
Their strategic priorities to improve faith and trust in higher education,
overcome systemic inequalities, and advance education to meet the changing
demands of students and community complement their members’ and the HE sector’s
initiatives.
Through their equality, diversity, and inclusion (EDI) mission, they are
specialists in higher education, with a special emphasis on improving teaching
and learning, effective governance, leadership creation, and addressing
inequality. Professional development programs and activities, fellowships,
awards, student assessments, strategic transformation and advisory options, and
membership are all forms they help (including accreditation of teaching and
learning, equality charters, research, knowledge and resources).
They collaborate with their global network of associates and partners, as well as
individuals, providers, and systems around the world, to identify contexts and
problems and provide solutions, drawing on their experience and exchanging best
practices.
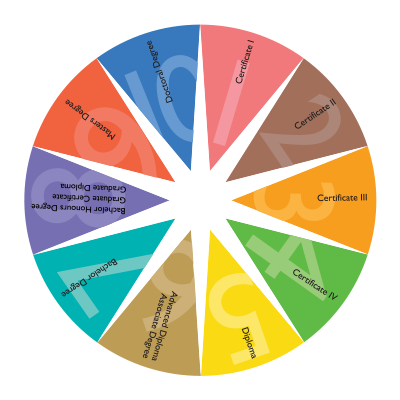
AQF Qualification
The broad discipline-free nomenclature used in the AQF to classify each category
of AQF certification, such as Senior Secondary Certificate of Education,
Certificate III, and Bachelor Degree, is alluded to as qualification type.
The conditions for AQF qualifications are included in each AQF certification
form, such as:
- the levels criteria
- the qualification type descriptor
- information about the responsibilities of qualification developers,
accrediting authorities and issuing organisations
The main reasons for having AQF certificates are to ensure national recognition
and consistency, as well as a common understanding of what each certification
entails across Australia.
Source
QILT
The Quality Indicators for Learning and Teaching (QILT) are a range of
government-backed surveys that span the whole student life cycle, from enrolment
to jobs. QILT provides reliable, globally consistent output data for Australian
higher education, allowing for quality enhancement to be pursued.
The Australian Government’s Department of Education, Skills and Jobs funds QILT.
Student Experience Survey Report 2020
ComparED
From the perspective of current students and new graduates, the ComparED website
provides potential students with appropriate and accessible knowledge about
Australian institutions of higher education. The information on the website is
based on survey findings from students who voluntarily provided feedback on
their overall experiences during their higher education studies, as well as the
outcomes of their career opportunities, such as starting salary. The content on
this website is designed to assist consumers in making well-informed decisions
about their future educational opportunities.
ComparED was designed to allow users to compare various organizations and
research areas using a variety of performance metrics gathered from QILT
surveys. The ComparED portal is driven by the QILT survey data and is financed
by the Australian Government Department of Education, Skills and Jobs.
IHM Postgraduate results 2020

















